Introduction
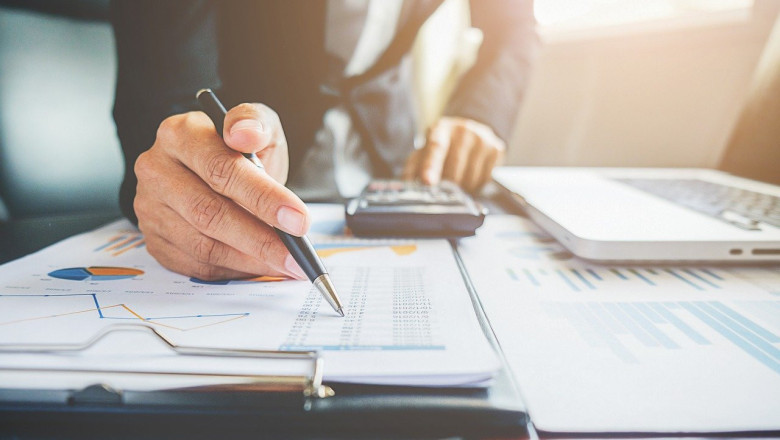
In today's competitive job market, the accuracy and authenticity of curriculum vitae (CV) applications are more critical than ever. Employers and hiring managers face the daunting task of sifting through numerous applications to identify the most qualified candidates. However, the prevalence of embellished or falsified information on CVs poses a significant challenge. Effective verification techniques are essential to ensure that the information presented by applicants is truthful and reliable.
This article delves into the various methods and strategies used to verify the details provided in CV applications. By understanding these techniques, employers can make more informed hiring decisions, reduce the risk of onboarding unqualified candidates, and maintain the integrity of their recruitment processes. From traditional reference checks to advanced digital verification tools, we will explore the best practices for ensuring the authenticity of CV information.
Importance of CV Verification Ensuring Accuracy and Authenticity
CV verification is crucial in ensuring the accuracy and authenticity of the information provided by candidates. Employers need to confirm that the qualifications, work experience, and skills listed on a CV are truthful and accurate. This process helps in identifying any discrepancies or false claims, which can prevent potential issues down the line.
Reducing Hiring Risks
Hiring the wrong candidate can be costly for an organization, both financially and in terms of time. CV verification helps mitigate these risks by ensuring that the candidate has the necessary qualifications and experience for the role. This reduces the likelihood of hiring someone who may not be capable of performing the job effectively.
Protecting Company Reputation
A company's reputation can be significantly impacted by the actions of its employees. By verifying CVs, employers can ensure that they are hiring individuals who are not only qualified but also have a history of ethical behavior. This helps in maintaining the integrity and reputation of the organization.
Enhancing Workplace Safety
In certain industries, such as healthcare, education, and finance, the accuracy of a candidate's qualifications and background is critical for ensuring workplace safety. Verifying CVs helps in confirming that candidates have the necessary certifications and training to perform their duties safely and effectively.
Legal Compliance
Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements that mandate thorough background checks and verification of employee credentials. CV verification helps organizations comply with these legal requirements, thereby avoiding potential legal issues and penalties.
Improving Hiring Efficiency
A thorough CV verification process can streamline the hiring process by quickly identifying the most qualified candidates. This allows HR teams to focus their efforts on candidates who have been verified, reducing the time and resources spent on unsuitable applicants.
Building Trust with Stakeholders
Stakeholders, including clients, investors, and partners, have a vested interest in the quality and integrity of an organization's workforce. By implementing a robust CV verification process, companies can build trust with their stakeholders, demonstrating their commitment to hiring qualified and trustworthy employees.
Enhancing Employee Morale
When employees know that their colleagues have been thoroughly vetted and verified, it can enhance overall morale and trust within the team. This creates a more positive and productive work environment, as employees feel confident in the capabilities and integrity of their peers.
Common Issues in CV Verification Inaccurate or Exaggerated Information Educational Background
One of the most common issues in CV verification is the exaggeration or falsification of educational qualifications. Candidates may claim degrees they have not earned or embellish their academic achievements. This can include listing institutions they never attended or inflating their GPA.
Employment History
Applicants often exaggerate their job titles, responsibilities, and achievements. They may extend the duration of their employment to cover gaps in their work history or claim experience in roles they never held. This can mislead employers about the candidate's actual experience and skills.
Fabricated References Fake Contacts
Some candidates provide fake references, listing friends or family members as former supervisors or colleagues. These references can give glowing but false endorsements, making it difficult for employers to get an accurate assessment of the candidate's past performance.
Unreachable References
Candidates may also provide references that are difficult to reach, either because they are no longer with the company or because the contact information is outdated. This can delay the verification process and make it challenging to confirm the candidate's credentials.
Inconsistent Information Discrepancies in Dates
Inconsistencies in employment dates are a red flag during CV verification. Candidates may alter dates to hide gaps in employment or to make their career progression appear more linear and impressive than it actually is.
Conflicting Job Titles and Responsibilities
Another common issue is the inconsistency between the job titles and responsibilities listed on the CV and those reported by references or found in public records. This can indicate that the candidate is not being truthful about their previous roles.
Lack of Documentation Missing Certificates and Transcripts
Candidates may fail to provide necessary documentation, such as certificates, diplomas, or transcripts, to verify their educational background. This can be due to lost documents or intentional omission to hide the lack of qualifications.
Unverifiable Employment Records
In some cases, candidates may list companies that have gone out of business or that do not have verifiable records. This makes it difficult to confirm their employment history and can raise questions about the authenticity of their claims.
Identity Verification Issues False Identity Claims
Some candidates may use false identities to apply for jobs, especially in industries where background checks are less stringent. This can lead to significant issues if the candidate is hired under false pretenses.
Inconsistent Personal Information
Discrepancies in personal information, such as different names or addresses on various documents, can complicate the verification process. This may indicate identity fraud or simply a lack of attention to detail, both of which are concerning for potential employers.
Legal and Ethical Concerns Privacy Violations
During the verification process, there is a risk of violating the candidate's privacy rights. Employers must navigate the legal landscape carefully to ensure they are compliant with data protection laws while verifying the information provided.
Discrimination Risks
There is also a risk of discrimination if the verification process is not conducted fairly and consistently. Employers must ensure that all candidates are subject to the same level of scrutiny to avoid potential legal issues and to maintain a fair hiring process.
Techniques for Effective Verification Automated Tools
Automated tools have revolutionized the process of CV verification by providing quick and efficient ways to validate the information provided by candidates. These tools can scan through large volumes of data and cross-reference it with various databases to ensure accuracy.
Benefits of Automated Tools
- Speed and Efficiency: Automated tools can process and verify information much faster than manual methods, allowing for quicker decision-making.
- Accuracy: These tools reduce human error by systematically checking data against reliable sources.
- Scalability: Automated systems can handle a large number of applications simultaneously, making them ideal for organizations that receive high volumes of CVs.
- Background Check Software: These tools can verify employment history, educational qualifications, and even criminal records.
- AI and Machine Learning Algorithms: Advanced algorithms can detect inconsistencies and flag potential issues for further investigation.
- Database Cross-Referencing: Tools that cross-reference information with professional databases, social media profiles, and other online resources to validate the authenticity of the data provided.
While automated tools offer numerous advantages, manual cross-checking remains an essential part of the verification process. Human oversight ensures that nuances and context, which automated systems might miss, are taken into account.
Steps in Manual Cross-Checking
- Document Verification: Manually reviewing certificates, transcripts, and other documents to ensure they are genuine and match the information provided in the CV.
- Interview Verification: Conducting follow-up interviews with the candidate to clarify any discrepancies or gather additional information.
- Online Research: Manually searching for the candidate's online presence, including social media profiles and professional networking sites, to cross-check the information provided.
- Contextual Understanding: Human reviewers can understand the context behind certain pieces of information, which automated tools might overlook.
- Nuanced Verification: Some aspects of a candidate's background, such as soft skills and personal attributes, are better assessed through human interaction.
- Error Correction: Manual checks can catch errors or inconsistencies that automated tools might miss, ensuring a more thorough verification process.
Reference checks are a critical component of CV verification, providing firsthand accounts of a candidate's past performance and behavior from previous employers or colleagues.
Conducting Effective Reference Checks
- Preparation: Before contacting references, prepare a list of specific questions that address the candidate's skills, work ethic, and suitability for the role.
- Consistency: Ask the same set of questions to all references to ensure consistency and comparability of the information gathered.
- Confidentiality: Ensure that the information shared by references is kept confidential and used solely for the purpose of verification.
- Employment History: Confirm the candidate's job titles, responsibilities, and duration of employment.
- Performance and Skills: Inquire about the candidate's job performance, key achievements, and any areas for improvement.
- Behavior and Attitude: Ask about the candidate's interpersonal skills, teamwork, and overall attitude in the workplace.
- Validation of Information: Reference checks provide an additional layer of validation, confirming the accuracy of the information provided in the CV.
- Insight into Work Ethic: References can offer valuable insights into the candidate's work ethic, reliability, and potential fit within the organization.
- Risk Mitigation: By thoroughly vetting candidates through reference checks, organizations can mitigate the risk of hiring individuals who may not meet the required standards.
Employers must ensure that their verification processes comply with anti-discrimination laws such as the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) guidelines in the United States. These laws prohibit discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age, disability, or genetic information. Verification processes should be applied uniformly to all candidates to avoid any form of bias or discrimination.
Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
In the United States, the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) regulates how employers can use consumer reports, including background checks, in the hiring process. Employers must obtain written consent from candidates before conducting background checks and must provide a copy of the report and a summary of rights if any adverse action is taken based on the report.
Data Protection and Privacy Laws
Employers must adhere to data protection and privacy laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. These laws require employers to handle personal data responsibly, ensuring it is collected, processed, and stored securely. Candidates must be informed about how their data will be used and have the right to access, correct, or delete their information.
Ethical Considerations in Verification Transparency and Consent
Transparency is crucial in the verification process. Employers should inform candidates about the verification procedures, the types of information that will be checked, and how the information will be used. Obtaining explicit consent from candidates before conducting any verification checks is essential to maintain trust and respect for their privacy.
Accuracy and Fairness
Employers have an ethical obligation to ensure the accuracy of the information obtained during the verification process. This includes cross-referencing multiple sources and giving candidates the opportunity to correct any inaccuracies. Fairness involves treating all candidates equally and avoiding any actions that could unfairly disadvantage a candidate based on incorrect or incomplete information.
Confidentiality
Maintaining the confidentiality of candidates' information is a critical ethical consideration. Employers must ensure that personal and sensitive information obtained during the verification process is kept secure and only accessible to authorized personnel. Breaching confidentiality can damage the candidate's trust and the employer's reputation.
Balancing Verification with Candidate Rights Right to Privacy
Candidates have a fundamental right to privacy, which must be balanced against the employer's need to verify information. Employers should limit the scope of verification to information that is directly relevant to the job and avoid intrusive checks that could infringe on the candidate's personal life.
Right to Explanation
Candidates should have the right to an explanation if they are not selected for a position based on the results of the verification process. Providing feedback helps candidates understand the reasons behind the decision and allows them to address any issues in future applications.
Right to Appeal
Employers should establish a clear process for candidates to appeal decisions made based on verification results. This process should allow candidates to present additional information or clarify any discrepancies, ensuring that decisions are fair and just.
Case Studies and Examples Case Study 1: Verifying Academic Credentials Background
A mid-sized tech company received an application from a candidate claiming to have a Master's degree in Computer Science from a prestigious university. The hiring manager decided to verify the academic credentials before proceeding with the interview process.
Verification Process
- Contacting the University: The HR department contacted the registrar's office of the university directly to confirm the candidate's degree.
- Third-Party Verification Service: The company also employed a third-party verification service to cross-check the information provided by the candidate.
The university confirmed that the candidate had indeed graduated with the claimed degree. The third-party service corroborated this information, providing additional details such as the graduation date and GPA. The candidate was then moved forward in the hiring process.
Case Study 2: Employment History Verification Background
A financial services firm received an application from a candidate who claimed to have worked as a Senior Analyst at a well-known investment bank for five years. Given the sensitive nature of the role, the firm decided to verify the candidate's employment history.
Verification Process
- Direct Contact: The HR team contacted the previous employer directly to verify the candidate's job title, duration of employment, and responsibilities.
- Reference Checks: The firm also reached out to the references provided by the candidate to gather more insights into their performance and work ethic.
The previous employer confirmed the candidate's job title and duration of employment but noted discrepancies in the responsibilities listed on the CV. The references provided mixed reviews, with some questioning the candidate's ability to handle high-pressure situations. Based on this information, the firm decided not to proceed with the candidate.
Case Study 3: Skills and Certifications Verification Background
A healthcare organization was hiring for a specialized role requiring specific certifications and skills in medical coding. The candidate claimed to have multiple certifications and extensive experience in the field.
Verification Process
- Certification Bodies: The HR team contacted the certification bodies to verify the authenticity of the candidate's certifications.
- Skills Assessment: The organization conducted a practical skills assessment to evaluate the candidate's proficiency in medical coding.
The certification bodies confirmed that the candidate held the claimed certifications. The skills assessment further validated the candidate's expertise, demonstrating a high level of proficiency. The candidate was successfully hired for the role.
Case Study 4: Social Media and Online Presence Background
A marketing agency received an application from a candidate who claimed to have extensive experience in social media management and digital marketing. The agency decided to verify the candidate's online presence and portfolio.
Verification Process
- Social Media Audit: The HR team conducted a thorough audit of the candidate's social media profiles, including LinkedIn, Twitter, and personal blog.
- Portfolio Review: The agency reviewed the candidate's portfolio, paying close attention to the campaigns and projects listed.
The social media audit revealed a strong online presence, with consistent professional branding and engagement in relevant industry discussions. The portfolio review confirmed the candidate's involvement in several successful campaigns, aligning with the claims made on the CV. The candidate was invited for an interview and subsequently hired.
Case Study 5: International Experience Verification Background
A multinational corporation was considering a candidate who claimed to have extensive international experience, including roles in Europe and Asia. The company needed to verify these claims due to the strategic importance of the role.
Verification Process
- International References: The HR team contacted the candidate's previous employers in Europe and Asia to verify job titles, responsibilities, and duration of employment.
- Cross-Cultural Competency Assessment: The company conducted an assessment to evaluate the candidate's cross-cultural competencies and adaptability.
The international references confirmed the candidate's employment history and provided positive feedback on their performance and adaptability. The cross-cultural competency assessment further validated the candidate's ability to work effectively in diverse environments. The candidate was offered the position.
Best Practices for Employers Establish Clear Verification Policies Define Verification Scope
Employers should clearly define the scope of verification processes. This includes specifying which aspects of a candidate's CV will be verified, such as employment history, educational qualifications, and professional certifications.
Standardize Procedures
Standardizing verification procedures ensures consistency and fairness. Develop a checklist or a set of guidelines that HR personnel can follow to verify each candidate's information systematically.
Utilize Reliable Verification Methods Direct Contact with Previous Employers
Contacting previous employers directly is one of the most reliable methods for verifying employment history. Ensure that you speak with someone who can confirm the candidate's job title, responsibilities, and dates of employment.
Educational Verification Services
Use third-party educational verification services to confirm the authenticity of a candidate's academic qualifications. These services can directly contact educational institutions to verify degrees and certifications.
Implement Technology Solutions Automated Verification Tools
Leverage automated verification tools that can quickly cross-check information provided in CVs against databases and public records. These tools can save time and reduce human error.
Blockchain for Credential Verification
Consider using blockchain technology for credential verification. Blockchain can provide a tamper-proof record of a candidate's qualifications and work history, ensuring the information is accurate and trustworthy.
Maintain Compliance with Legal and Ethical Standards Data Privacy Regulations
Ensure that your verification processes comply with data privacy regulations such as GDPR or CCPA. Obtain explicit consent from candidates before conducting any background checks or verifications.
Ethical Considerations
Maintain ethical standards by being transparent with candidates about the verification process. Inform them about what will be verified and how the information will be used.
Train HR Personnel verification Techniques
Provide training for HR personnel on effective verification techniques. This includes how to conduct interviews with previous employers, how to use verification tools, and how to interpret the results.
Legal and Ethical Training
Ensure that HR staff are well-versed in legal and ethical considerations related to verification. This training should cover data privacy laws, anti-discrimination laws, and ethical guidelines for handling candidate information.
Document and Review Verification Processes Record Keeping
Maintain detailed records of all verification activities. This includes notes from conversations with previous employers, results from verification services, and any discrepancies found.
Regular Audits
Conduct regular audits of your verification processes to ensure they are effective and compliant with legal standards. Use audit results to make necessary improvements to your procedures.
Foster a Culture of HonestyEncourage Transparency
Encourage candidates to be transparent by fostering a culture of honesty within your organization. Make it clear that providing accurate information is crucial and that discrepancies will be addressed fairly.
Address Discrepancies
When discrepancies are found, address them promptly and fairly. Give candidates an opportunity to explain any inconsistencies and consider their explanations before making a final decision.
Future Trends in CV Verification Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing CV verification by automating the process and increasing accuracy. These technologies can quickly scan and analyze large volumes of CVs, identifying inconsistencies and potential red flags. Machine learning algorithms can be trained to recognize patterns and anomalies that might indicate fraudulent information, such as discrepancies in employment dates or educational qualifications.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain offers a secure and transparent way to verify credentials. By storing educational and professional records on a blockchain, employers can easily verify the authenticity of a candidate's qualifications. This technology ensures that the data is tamper-proof and can be accessed in real-time, reducing the risk of fraud and making the verification process more efficient.
Biometric Verification
Biometric verification, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, is becoming more prevalent in CV verification. This technology can be used to confirm the identity of a candidate, ensuring that the person submitting the CV is indeed who they claim to be. Biometric data can be cross-referenced with official records to further validate the candidate's identity and credentials.
Enhanced Data Analytics
Advanced data analytics tools are being developed to provide deeper insights into a candidate's background. These tools can analyze social media profiles, online presence, and other digital footprints to build a comprehensive picture of the candidate. This holistic approach helps employers to verify not just the factual accuracy of a CV, but also to assess the candidate's professional reputation and cultural fit.
Integration with Social Media and Professional Networks
Integration with platforms like LinkedIn and other professional networks allows for real-time verification of a candidate's work history and endorsements. Employers can cross-check the information provided in a CV with the candidate's online profiles, ensuring consistency and authenticity. This trend also leverages the power of peer endorsements and recommendations, adding another layer of verification.
Real-Time Verification Services
Real-time verification services are emerging as a key trend, providing instant validation of a candidate's credentials. These services can access various databases and records to verify educational qualifications, employment history, and other critical information in real-time. This reduces the time and effort required for manual verification and ensures that employers have up-to-date information.
Regulatory Compliance and Data Privacy
As data privacy regulations become more stringent, CV verification processes must adapt to ensure compliance. Future trends will likely include more robust data protection measures and transparent consent mechanisms. Employers will need to balance the need for thorough verification with the requirement to protect candidate privacy and comply with legal standards.
Gamification and Interactive Assessments
Gamification and interactive assessments are being integrated into the CV verification process to evaluate a candidate's skills and competencies in a more engaging way. These tools can provide real-time feedback and validation of a candidate's abilities, offering a dynamic alternative to traditional CV verification methods. This trend not only enhances the verification process but also improves the candidate experience.