Introduction
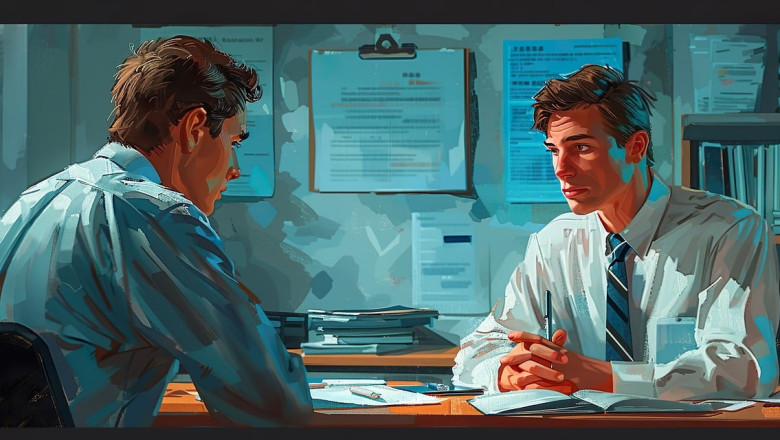
In today's dynamic business environment, the role of a Finance Business Partner (FBP) has evolved beyond traditional financial management. FBPs are now integral to strategic decision-making, acting as a bridge between finance and other business functions. This shift necessitates a deep understanding of both financial principles and the operational aspects of the business.
Effective cross-functional collaboration is essential for FBPs to drive value and support organizational goals. By working closely with various departments, FBPs can provide insights that enhance performance, optimize resources, and foster innovation. This article explores the key strategies and best practices for FBPs to enhance cross-functional collaboration, ensuring they contribute effectively to the business's success.
Understanding the Role of a Finance Business PartnerStrategic Advisor
A Finance Business Partner (FBP) acts as a strategic advisor to the business, providing insights and recommendations that drive decision-making. They analyze financial data to identify trends, opportunities, and risks, and translate these findings into actionable business strategies. By understanding the broader business context, FBPs help align financial goals with the company's strategic objectives, ensuring that financial considerations are integrated into the overall business plan.
Financial Planning and Analysis
FBPs are deeply involved in financial planning and analysis (FP&A). They work on budgeting, forecasting, and financial modeling to predict future financial performance. This involves collaborating with various departments to gather data, assess financial implications, and create comprehensive financial plans. Their expertise in FP&A helps the business set realistic financial targets and track performance against these goals, enabling proactive management of financial resources.
Performance Monitoring
Monitoring business performance is a critical aspect of the FBP role. They develop key performance indicators (KPIs) and other metrics to measure the financial health of the organization. By regularly reviewing these metrics, FBPs can identify areas of underperformance and recommend corrective actions. This continuous monitoring ensures that the business stays on track to meet its financial objectives and can quickly adapt to changing circumstances.
Risk Management
FBPs play a crucial role in identifying and managing financial risks. They assess potential risks related to market fluctuations, operational inefficiencies, and other factors that could impact the business's financial stability. By developing risk mitigation strategies and contingency plans, FBPs help safeguard the company's financial health. Their proactive approach to risk management ensures that the business is prepared to handle uncertainties and can maintain financial resilience.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Effective cross-functional collaboration is essential for FBPs. They work closely with various departments, such as marketing, operations, and human resources, to understand their financial needs and challenges. By fostering strong relationships and open communication, FBPs ensure that financial insights are integrated into all aspects of the business. This collaborative approach helps create a unified strategy that supports the company's overall goals.
Communication and Influence
FBPs must possess strong communication and influencing skills. They need to convey complex financial information in a clear and concise manner to non-financial stakeholders. This involves presenting financial reports, explaining the implications of financial data, and making persuasive arguments for strategic decisions. Their ability to influence others ensures that financial considerations are given due weight in the decision-making process.
Continuous Improvement
FBPs are committed to continuous improvement, both in their own skills and in the financial processes of the organization. They stay updated with the latest financial tools, technologies, and best practices to enhance their effectiveness. By promoting a culture of continuous improvement, FBPs help the business optimize its financial operations, drive efficiency, and achieve better financial outcomes.
Building Strong Relationships with Business UnitsUnderstanding Business Needs and Goals
To build strong relationships with business units, it is crucial to first understand their specific needs and goals. This involves:
- Conducting Regular Meetings: Schedule regular meetings with key stakeholders to discuss their objectives, challenges, and expectations. This helps in gaining a deeper insight into their operational priorities and strategic goals.
- Listening Actively: Pay close attention to the concerns and suggestions of business unit leaders. Active listening fosters trust and demonstrates a genuine interest in their success.
- Tailoring Financial Insights: Customize financial reports and insights to align with the unique needs of each business unit. This ensures that the information provided is relevant and actionable.
Effective communication is the cornerstone of any strong relationship. To enhance communication with business units:
- Clear and Concise Reporting: Provide clear, concise, and jargon-free financial reports. Use visual aids like charts and graphs to make complex data more understandable.
- Open Channels of Communication: Establish open lines of communication through various channels such as emails, instant messaging, and face-to-face meetings. Encourage business units to reach out with any questions or concerns.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implement feedback mechanisms to continuously improve the quality of communication. Regularly seek input from business units on how financial information can be better presented and more useful.
Trust and credibility are essential for a successful partnership. To build these:
- Consistency and Reliability: Deliver accurate and timely financial information consistently. Reliability in your work builds confidence among business units.
- Transparency: Be transparent about financial processes, methodologies, and any limitations in the data. Transparency fosters trust and reduces misunderstandings.
- Proactive Support: Offer proactive support by identifying potential financial risks and opportunities before they become apparent to the business units. This demonstrates a commitment to their success.
Collaborative problem solving strengthens relationships by showing that you are a partner in overcoming challenges. To foster collaboration:
- Joint Planning Sessions: Participate in joint planning sessions to align financial strategies with business unit goals. This ensures that financial plans are supportive of operational objectives.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Form cross-functional teams to tackle specific issues or projects. This encourages a collaborative approach and leverages diverse expertise.
- Shared Accountability: Promote shared accountability for financial outcomes. When business units see that you are equally invested in their success, it strengthens the partnership.
The business environment is dynamic, and continuous learning and adaptation are key to maintaining strong relationships. To stay relevant:
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of industry trends, market conditions, and regulatory changes that may impact business units. This knowledge allows you to provide timely and relevant advice.
- Professional Development: Engage in ongoing professional development to enhance your financial expertise and soft skills. This ensures that you can offer the best possible support to business units.
- Adapt to Feedback: Be willing to adapt your approach based on feedback from business units. Continuous improvement in your methods and communication style will strengthen the relationship over time.
Recognize who your key stakeholders are within the business. This includes senior management, department heads, and team leaders. Understanding their roles, responsibilities, and priorities will help tailor your communication to meet their specific needs.
Tailoring Messages
Customize your communication style and content based on the audience. For instance, senior management may prefer high-level summaries with strategic insights, while department heads might need more detailed financial data and analysis.
Active ListeningEncouraging Feedback
Create an environment where stakeholders feel comfortable providing feedback. This can be achieved through regular check-ins, surveys, or informal conversations. Listening to their concerns and suggestions can provide valuable insights and foster a collaborative atmosphere.
Reflective Listening
Practice reflective listening by paraphrasing what the other person has said to ensure understanding. This not only clarifies the message but also shows that you value their input.
Clear and Concise MessagingSimplifying Complex Information
Break down complex financial data into simple, digestible information. Use visuals like charts, graphs, and infographics to make the data more accessible and easier to understand.
Avoiding Jargon
Use plain language and avoid technical jargon that may not be familiar to all stakeholders. This ensures that your message is clear and comprehensible to everyone involved.
Regular Updates and ReportingScheduled Meetings
Establish a regular meeting schedule to provide updates on financial performance, forecasts, and other relevant information. Consistent communication helps keep everyone aligned and informed.
Real-Time Reporting
Utilize real-time reporting tools to provide up-to-date financial information. This allows stakeholders to make informed decisions based on the most current data available.
Leveraging TechnologyCollaboration Tools
Use collaboration tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Trello to facilitate communication and project management. These platforms can help streamline workflows and ensure that everyone is on the same page.
Data Visualization Software
Implement data visualization software such as Tableau or Power BI to present financial data in a more engaging and understandable format. Visual aids can significantly enhance the clarity of your communication.
Building RelationshipsOne-on-One Meetings
Schedule regular one-on-one meetings with key stakeholders to build rapport and trust. Personalized interactions can help you better understand their needs and concerns.
Cross-Functional Workshops
Organize cross-functional workshops to encourage collaboration and open dialogue between different departments. These sessions can help break down silos and foster a more integrated approach to problem-solving.
Emotional IntelligenceEmpathy
Show empathy by understanding and acknowledging the challenges and pressures that other departments face. This can help build stronger relationships and improve collaboration.
Managing Conflict
Develop skills to manage and resolve conflicts effectively. Addressing issues promptly and diplomatically can prevent misunderstandings and maintain a positive working environment.
Leveraging Data and Analytics for Decision MakingUnderstanding the Role of Data in Finance
Data is the backbone of informed decision-making in finance. As a Finance Business Partner, your ability to interpret and leverage data can significantly impact the strategic direction of the business. Data provides insights into financial performance, market trends, and operational efficiencies, enabling you to make evidence-based recommendations.
Types of Data and AnalyticsFinancial Data
Financial data includes income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and other financial reports. This data helps in understanding the financial health of the organization, identifying trends, and forecasting future performance.
Operational Data
Operational data encompasses metrics related to the day-to-day activities of the business, such as production rates, supply chain efficiency, and employee productivity. This data is crucial for identifying areas where operational improvements can lead to cost savings and increased efficiency.
Market Data
Market data includes information about industry trends, competitor performance, and customer behavior. This data helps in understanding the external environment and making strategic decisions that align with market conditions.
Tools and Technologies for Data AnalysisBusiness Intelligence (BI) Tools
BI tools like Tableau, Power BI, and QlikView allow you to visualize data and create interactive dashboards. These tools help in identifying trends, patterns, and anomalies in the data, making it easier to communicate insights to stakeholders.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to forecast future outcomes based on historical data. Tools like SAS, IBM SPSS, and Python libraries can be used to build predictive models that help in budgeting, forecasting, and risk management.
Data Warehousing
Data warehousing solutions like Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Snowflake provide a centralized repository for storing and managing large volumes of data. These solutions enable efficient data retrieval and analysis, supporting real-time decision-making.
Best Practices for Data-Driven Decision MakingData Quality and Governance
Ensuring data quality and governance is critical for reliable decision-making. Implement data validation processes, establish data governance policies, and regularly audit data sources to maintain accuracy and consistency.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Collaborate with other departments to gather comprehensive data and insights. Working closely with marketing, operations, and HR teams can provide a holistic view of the business, enabling more informed decisions.
Continuous Monitoring and Reporting
Implement continuous monitoring and reporting mechanisms to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and other critical metrics. Regularly review and update reports to reflect the latest data, ensuring that decisions are based on current information.
Case Studies and ExamplesCase Study: Improving Cash Flow Management
A manufacturing company used predictive analytics to forecast cash flow more accurately. By analyzing historical financial data and market trends, the finance team identified periods of potential cash shortages and implemented strategies to mitigate risks, resulting in improved liquidity and financial stability.
Example: Enhancing Operational Efficiency
An e-commerce business leveraged BI tools to analyze operational data, identifying bottlenecks in the supply chain. By visualizing data on a dashboard, the finance team collaborated with the operations department to streamline processes, reducing delivery times and operational costs.
Challenges and SolutionsData Silos
Data silos can hinder effective data analysis and decision-making. Implement integrated data management systems and promote a culture of data sharing across departments to break down silos.
Skill Gaps
A lack of data analytics skills can be a barrier to leveraging data effectively. Invest in training and development programs to enhance the analytical capabilities of the finance team, ensuring they can effectively use data and analytics tools.
Data Privacy and Security
Ensuring data privacy and security is paramount. Implement robust data protection measures, comply with relevant regulations, and regularly review security protocols to safeguard sensitive information.
Driving Strategic Initiatives and Business PerformanceUnderstanding Business Objectives
A Finance Business Partner (FBP) must have a deep understanding of the company's strategic objectives. This involves aligning financial goals with the broader business strategy, ensuring that financial planning and analysis support the company's long-term vision. By comprehending the core objectives, FBPs can provide insights that drive strategic decision-making and enhance overall business performance.
Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
To effectively drive strategic initiatives, FBPs need to identify and monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with the company's strategic goals. These KPIs should be both financial and non-financial, providing a comprehensive view of the business's health. Regularly tracking these metrics allows FBPs to identify trends, forecast future performance, and make data-driven recommendations.
Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A)
FP&A is a critical function for driving strategic initiatives. FBPs should engage in robust financial planning, budgeting, and forecasting processes. This involves creating detailed financial models that project future performance based on various scenarios. By analyzing these models, FBPs can identify potential risks and opportunities, enabling proactive management of the business's financial health.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Effective cross-functional collaboration is essential for driving strategic initiatives. FBPs should work closely with other departments, such as marketing, operations, and human resources, to ensure that financial strategies are integrated into all aspects of the business. This collaboration helps to align departmental goals with the overall business strategy, fostering a unified approach to achieving the company's objectives.
Strategic Cost Management
FBPs play a crucial role in strategic cost management, identifying areas where the company can reduce costs without compromising on quality or performance. This involves analyzing cost structures, benchmarking against industry standards, and implementing cost-saving initiatives. By managing costs strategically, FBPs can improve the company's profitability and competitive position.
Investment Appraisal and Capital Allocation
FBPs are responsible for evaluating potential investments and capital allocation decisions. This involves conducting thorough financial analysis to assess the viability and potential return on investment (ROI) of various projects. By prioritizing investments that align with the company's strategic goals, FBPs can ensure that resources are allocated effectively to drive business growth.
Performance Monitoring and Reporting
Regular performance monitoring and reporting are essential for driving strategic initiatives. FBPs should develop comprehensive reporting frameworks that provide real-time insights into the company's financial performance. These reports should be tailored to the needs of different stakeholders, ensuring that decision-makers have the information they need to make informed choices.
Continuous Improvement and Innovation
FBPs should foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within the finance function and across the organization. This involves staying abreast of industry trends, adopting new technologies, and implementing best practices. By continuously seeking ways to improve processes and drive innovation, FBPs can enhance the company's strategic capabilities and overall performance.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Cross-Functional CollaborationMisaligned Objectives and Priorities
One of the most significant challenges in cross-functional collaboration is the misalignment of objectives and priorities between departments. Each function within a business often has its own set of goals, which may not always align with the broader organizational objectives. This misalignment can lead to conflicts and inefficiencies.
Strategies to Align Objectives:
- Unified Vision and Goals: Establish a clear, unified vision and set of goals that all departments can work towards. This helps ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same end result.
- Regular Communication: Hold regular meetings to discuss progress, challenges, and changes in priorities. This keeps everyone informed and aligned.
- Integrated Planning: Develop integrated plans that consider the objectives and constraints of all departments. This ensures that plans are realistic and achievable.
Effective communication is crucial for successful cross-functional collaboration. However, communication barriers such as jargon, differing communication styles, and lack of transparency can hinder collaboration.
Strategies to Improve Communication:
- Common Language: Develop a common language or glossary of terms that everyone understands. This reduces misunderstandings and ensures clarity.
- Open Channels: Create open channels of communication where team members can freely share information and feedback. Tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or regular face-to-face meetings can facilitate this.
- Training: Provide training on effective communication skills, including active listening, clear articulation of ideas, and constructive feedback.
Cultural differences between departments can also pose a challenge. Each department may have its own culture, values, and ways of working, which can lead to misunderstandings and conflicts.
Strategies to Bridge Cultural Gaps:
- Cultural Awareness: Promote cultural awareness and sensitivity training to help team members understand and respect each other's differences.
- Team-Building Activities: Organize team-building activities that bring together members from different departments. This helps build trust and understanding.
- Cross-Functional Teams: Create cross-functional teams for specific projects. This encourages collaboration and helps break down cultural barriers.
Resource constraints, such as limited budgets, time, and personnel, can hinder cross-functional collaboration. Departments may compete for the same resources, leading to conflicts and inefficiencies.
Strategies to Manage Resources:
- Resource Planning: Develop a comprehensive resource plan that allocates resources based on the priorities and needs of all departments. This ensures fair distribution and optimal use of resources.
- Shared Resources: Identify opportunities for sharing resources between departments. This can include shared personnel, technology, or budget allocations.
- Prioritization: Prioritize projects and tasks based on their impact on the overall business objectives. This helps ensure that critical initiatives receive the necessary resources.
Resistance to change is a common challenge in any collaborative effort. Team members may be reluctant to adopt new processes, technologies, or ways of working.
Strategies to Overcome Resistance:
- Change Management: Implement a structured change management process that includes clear communication, training, and support. This helps team members understand the benefits of the change and how to adapt.
- Involvement: Involve team members in the decision-making process. This gives them a sense of ownership and reduces resistance.
- Incentives: Provide incentives for adopting new processes or technologies. This can include recognition, rewards, or career development opportunities.
A lack of accountability can lead to missed deadlines, poor performance, and finger-pointing. Without clear accountability, it is difficult to track progress and hold team members responsible for their contributions.
Strategies to Enhance Accountability:
- Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Define clear roles and responsibilities for each team member. This ensures that everyone knows what is expected of them.
- Performance Metrics: Establish performance metrics and KPIs to track progress and measure success. This provides a clear benchmark for accountability.
- Regular Reviews: Conduct regular performance reviews to assess progress, provide feedback, and address any issues. This helps keep everyone on track and accountable.
A Finance Business Partner plays a crucial role in bridging the gap between finance and other business units. By understanding the strategic objectives and operational challenges of different departments, they can provide valuable financial insights and support that drive business success.
Building Strong Relationships with Business Units
Establishing trust and rapport with business units is essential for effective collaboration. Regular interactions, active listening, and demonstrating a genuine interest in the goals and challenges of other departments help in building strong, productive relationships.
Effective Communication Strategies
Clear and concise communication is key to ensuring that financial insights are understood and acted upon. Tailoring the communication style to the audience, using visual aids, and simplifying complex financial data can enhance understanding and foster better decision-making.
Leveraging Data and Analytics for Decision Making
Utilizing data and analytics allows Finance Business Partners to provide actionable insights that can drive strategic decisions. By leveraging advanced analytical tools and techniques, they can identify trends, forecast outcomes, and measure performance, thereby adding significant value to the business.
Driving Strategic Initiatives and Business Performance
Finance Business Partners are instrumental in driving strategic initiatives that enhance business performance. By aligning financial goals with business strategies, they help in prioritizing investments, optimizing resources, and achieving long-term objectives.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Cross-Functional Collaboration
Cross-functional collaboration often comes with challenges such as differing priorities, communication barriers, and resistance to change. Addressing these challenges through proactive problem-solving, fostering a collaborative culture, and continuous learning can lead to more effective partnerships and better business outcomes.